Describe Three Processes That Fix Atmospheric Nitrogen
The nitrogen cycle involves three major steps. Ammonia can be used directly as fertilizer but most of it is further processed to urea and ammonium nitrate NH 4 NO 3.

Methods To Fix Atmospheric Dinitrogen A Comparison Of N2 Fixation By Download Scientific Diagram
Three processes are responsible for most of the nitrogen fixation in the biosphere.
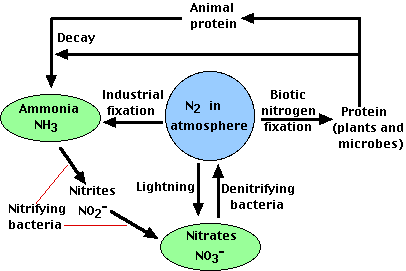
. The nitrogen cycle contains several steps such as nitrogen fixation assimilation ammonification nitrification and denitrification. Identify three processes that fix atmospheric nitrogen. The third process is biological.
Nitrogen fixation nitrification and denitrification. Under great pressure at a temperature of 600C and with the use of a catalyst atmospheric nitrogen and hydrogen usually derived from natural gas or petroleum can be combined to form ammonia NH 3. In the first approach air or any other uncombined mixture of oxygen and nitrogen is heated to a very high temperature and a small portion of the mixture reacts to form the gas nitric oxide.
The nitrogen molecule N 2 is quite inert. Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting the atmospheric nitrogen N 2 into biological state nitrogen. 1 has been significantly altered over the past century.
Identify three processes that fix atmospheric nitrogen lightning nitrogen fixation nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria identify the main geological reservoir that provides a source of nitrogen. It is a cycle within the biosphere which involves the atmosphere hydrosphere and lithosphere. During lightning the high temperatures and pressures created in the air convert nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen.
Five main processes cycle nitrogen through the biosphere atmosphere and geosphere. Nitrogen fixation N2 - NH4 nitrogen uptake NH4 - Organic N nitrogen mineralization Organic N - NH4 nitrification NH4 - NO3- and denitrification NO3 - NO2 - NO - N2O - N2. Nitrogenase is made up of two soluble proteins.
The three most-productive approaches were the direct combination of nitrogen with oxygen the reaction of nitrogen with calcium carbide and the direct combination of nitrogen with hydrogen. Nitrogen may be fixed via natural or synthetic processes. Lightning biological fixation and industrial fixation Thunder biological fixation and rain fixation Fixation by bacteria lightning and fixation by animals Industrial fixation lightning and ammonia decomposition All of the answers are correct.
Correspondingly what is the process of nitrogen fixation. And by other natural phenomena. It is the first process of making nitrogen available for plants.
And 26 to 28 acid labile sulfidesalso known as iron-molybdenum cofactor. In this process nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia another form of nitrogen by certain bacterial species like Rhizobium Azotobacter etc. It is most prevalent in sediments and rocks second in the atmosphere 78.
Process of Nitrogen Cycle consists of the following steps Nitrogen fixation Nitrification Assimilation Ammonification and Denitrification. Atmospheric fixation by lightning industrial fixation. Rain and snow carry these compounds to the surface where plants use them.
Biological nitrogen fixation occurs atmospheric nitrogen is converted Ammonia by an enzyme called nitrogenase. The process is solely carried out by prokaryotes bacteria which have. There is only one.
Therefore it must be converted to an organic or fixed form in a process called nitrogen fixation. Some prokaryotes such as bacteria and cyanobacteria that can fix atmospheric nitrogen are called nitrogen fixers or diazotrophs. The three ways of nitrogen fixation are.
Lightning ammonia production nitrogen fixing bacteria Process that releases nitrogen gas into the atmosphere. Component 1 is known as MoFe protein or nitrogenase contains 2 Mo atoms 28-34 iron atoms. Atmospheric nitrogen is molecular dinitrogen a relatively nonreactive molecule that is metabolically useless to all but a few microorganisms.
Biological nitrogen fixation BNF occurs when atmospheric nitrogen is converted to ammonia by an enzyme called nitrogenase. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide N 2 O mole fractions have increased from a pre. Biological nitrogen fixation was discovered by the German agronomist Hermann Hellriegel and Dutch microbiologist Martinus Beijerinck.
These processes take place in several stages and are explained below. Biological Nitrogen Fixation. Component 1 and 2.
There are two key methods of natural nitrogen fixation. The three methods of nitrogen fixation are. The process of conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds by microorganisms such as bacteria fungi and algae is known as Biological Nitrogen Fixation BNF or diazotrophy.
Atmospheric nitrogen occurs primarily in an inert form N2 that few organisms can use. Nitrogen is found in several locations or reservoirs. Nitrogen fixation is the essential biological process and the initial stage of the nitrogen cycle.
The reduction of free atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia by living organisms is called biological nitrogen fixation. Only certain prokaryotic bacterias are capable of fixing nitrogen. Three processes are responsible for most of the nitrogen.
To break it apart so that its atoms can combine with other atoms requires the input of substantial amounts of energy. Biological nitrogen fixation BNF is the process whereby atmospheric nitrogen is reduced to ammonia in the presence of nitrogenize. Lightning provides energy to react water H 2 O and nitrogen gas N 2 to form nitrates NO 3 and ammonia NH 3.
As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs the global nitrogen cycle Fig. Biological nitrogen fixation or diazotrophy is an important microbially mediated process that converts dinitrogen N 2 gas to ammonia NH 3 using the nitrogenase protein complex Nif. The process of conversion of atmospheric inert nitrogen gas to fixed nitrogen inorganic compounds usable by plants that is ammonia is termed Nitrogen Fixation.
Nitrogenize is a biological catalyst found naturally only in certain microorganisms such as the symbiotic Rhizobium and Frankia or the free-living Azospirillum and Azotobacter and BGA. Nitrogenases are enzymes used by some organisms to fix atmospheric nitrogen gas N 2. I Atmospheric nitrogen fixation.
It is defined as an anaerobic without oxygen process that catalyzes the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen N 2 into ammonia NH 3. Agricultural and industrial nitrogen N inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. Human impact on the nitrogen cycle is diverse.
The nitrogen cycle is a cyclic process where the nitrogen travels from inorganic form in the atmosphere and to the organic way in the living organisms.

17 2b Nitrogen Cycle Biology Libretexts

5 15a Nitrogenase And Nitrogen Fixation Biology Libretexts

Nitrogen Fixation Definition Process Examples Types Facts Britannica
No comments for "Describe Three Processes That Fix Atmospheric Nitrogen"
Post a Comment